It was the best of times. It was the worst of times.
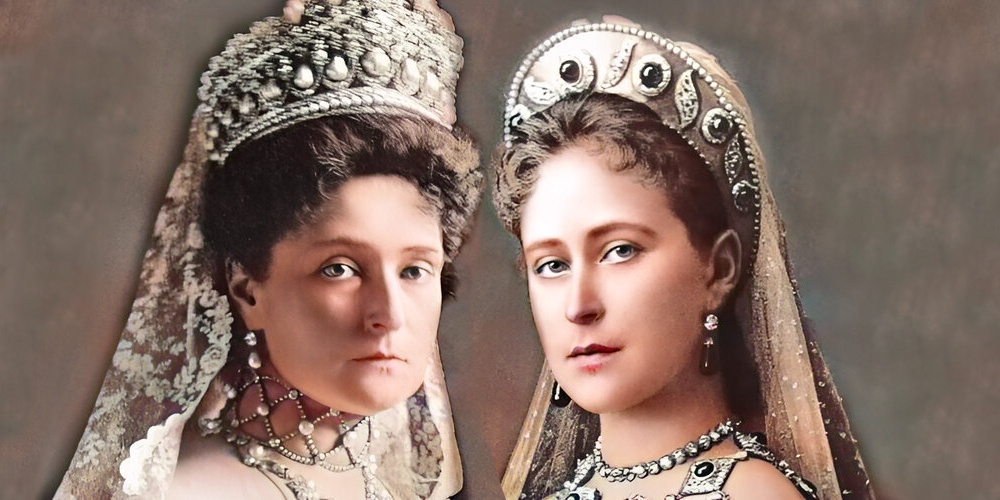
This is the tragic story of two sisters.
Two beautiful Russian princesses who lived fairy tale lives.
Until one fateful day in 1918.
The Best of Times
To be a princess in Victorian-era Europe meant you were born with a silver spoon and you joined a set of elites—life’s lucky lottery winners.
Endless balls and parties, changing from one costume to the next.
Life was a dream, a fairytale.
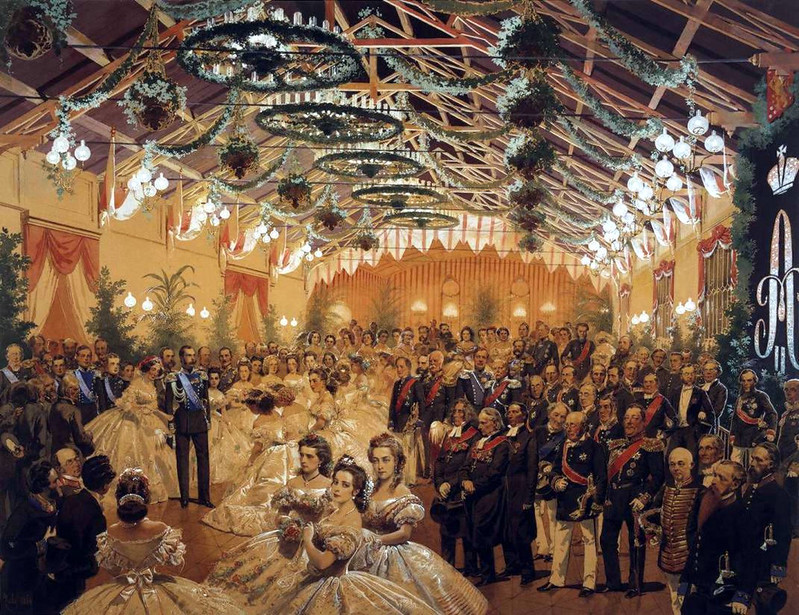

Theatre, ballet, opera, concerts, sporting events, afternoon tea.
Such a hectic social calendar and so little time.
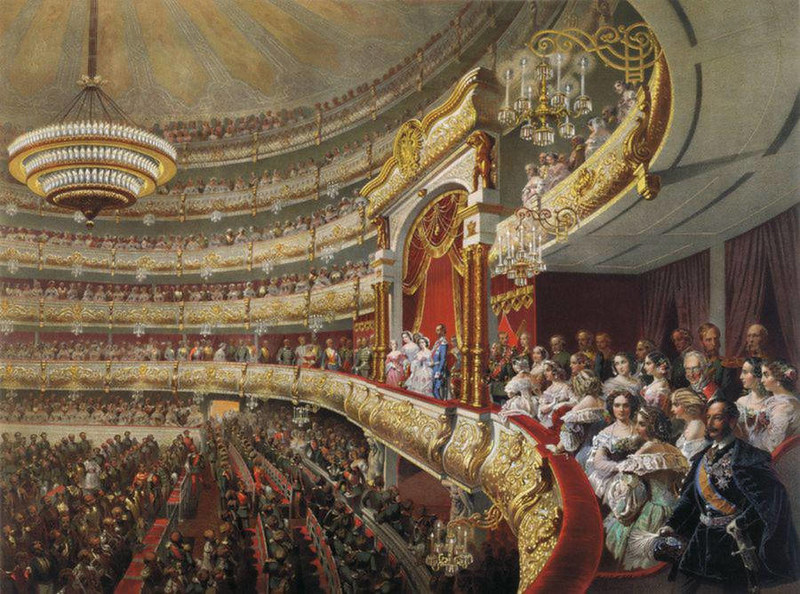

Wealthy noble suitors professed their love, proposed, and showered you with the finest gifts.
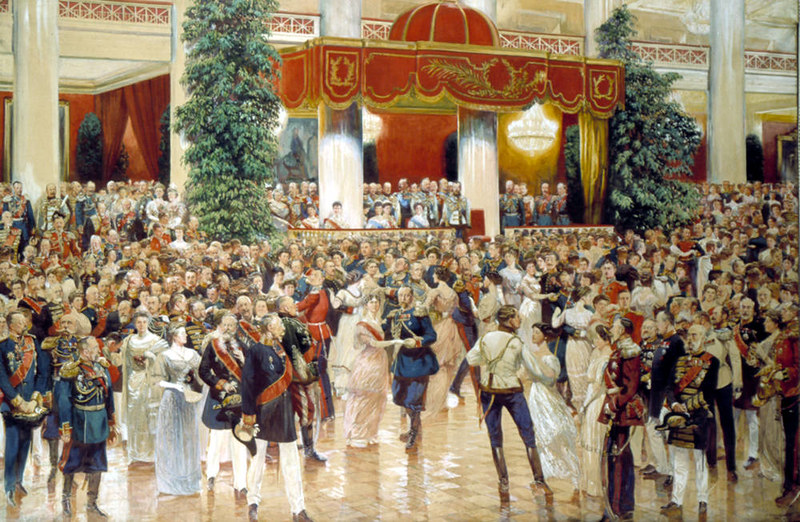

These were halcyon days enjoyed by the few. The best of times.
The Worst of Times
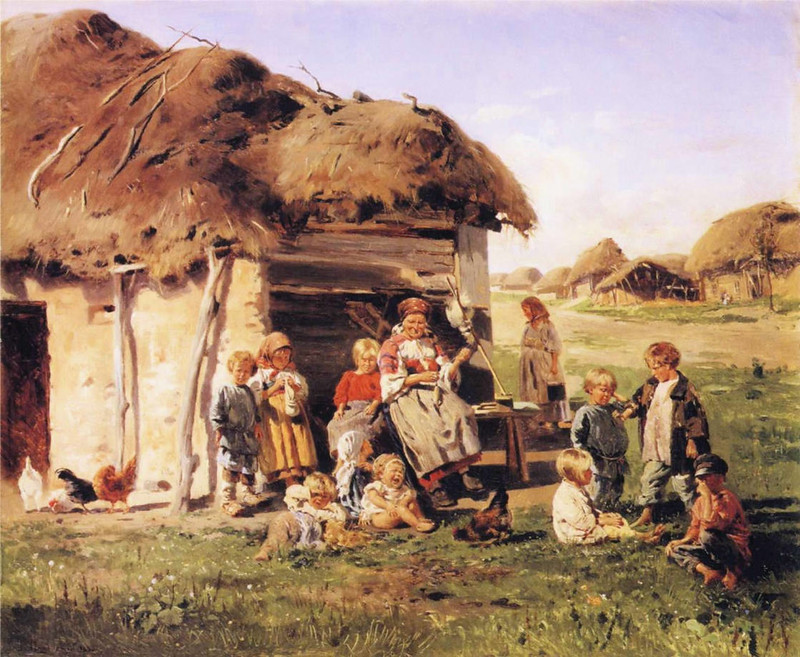
Being poor in 19th-century Europe was not something to be recommended.
To be a peasant in Russia was about as harsh as it could get.
But life was a game of chance and if you were that unfortunate, you were not alone.
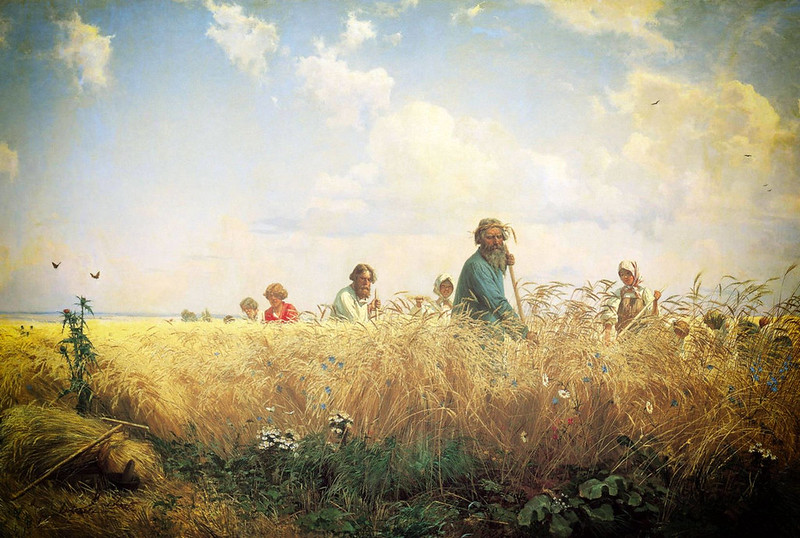

Ninety-Five percent of Russians were poor peasants who owned no land.
They paid high rents to landlords who just happened to be members of the ruling aristocracy.
Living in little more than mud huts in villages cut off from the world, the illiterate peasants worked the land to scrape a living to survive and pay their rent.

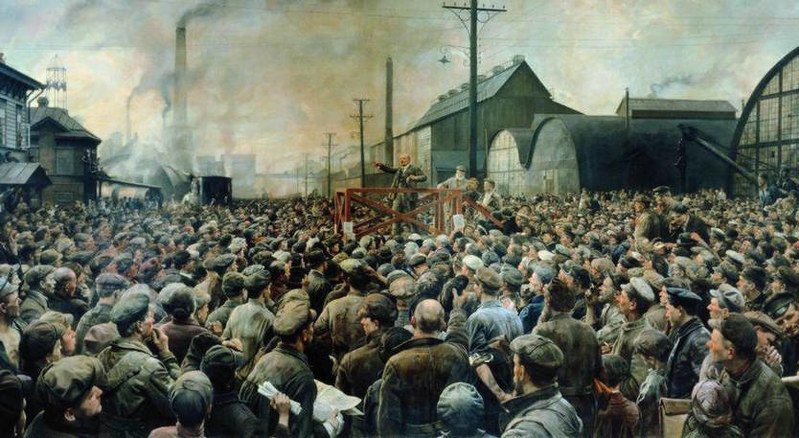
When the Industrial Revolution came to Russia, poverty followed the people from the countryside to the cities.
Factories were dark, dirty, and dangerous.
Low wages and long hours kept the former peasants in their place and they were drawn to speeches by men with ideas on changing the world and the promise of a better life.

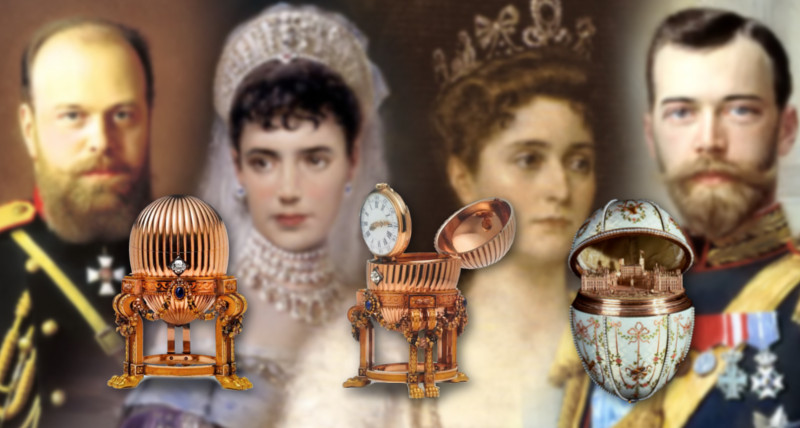
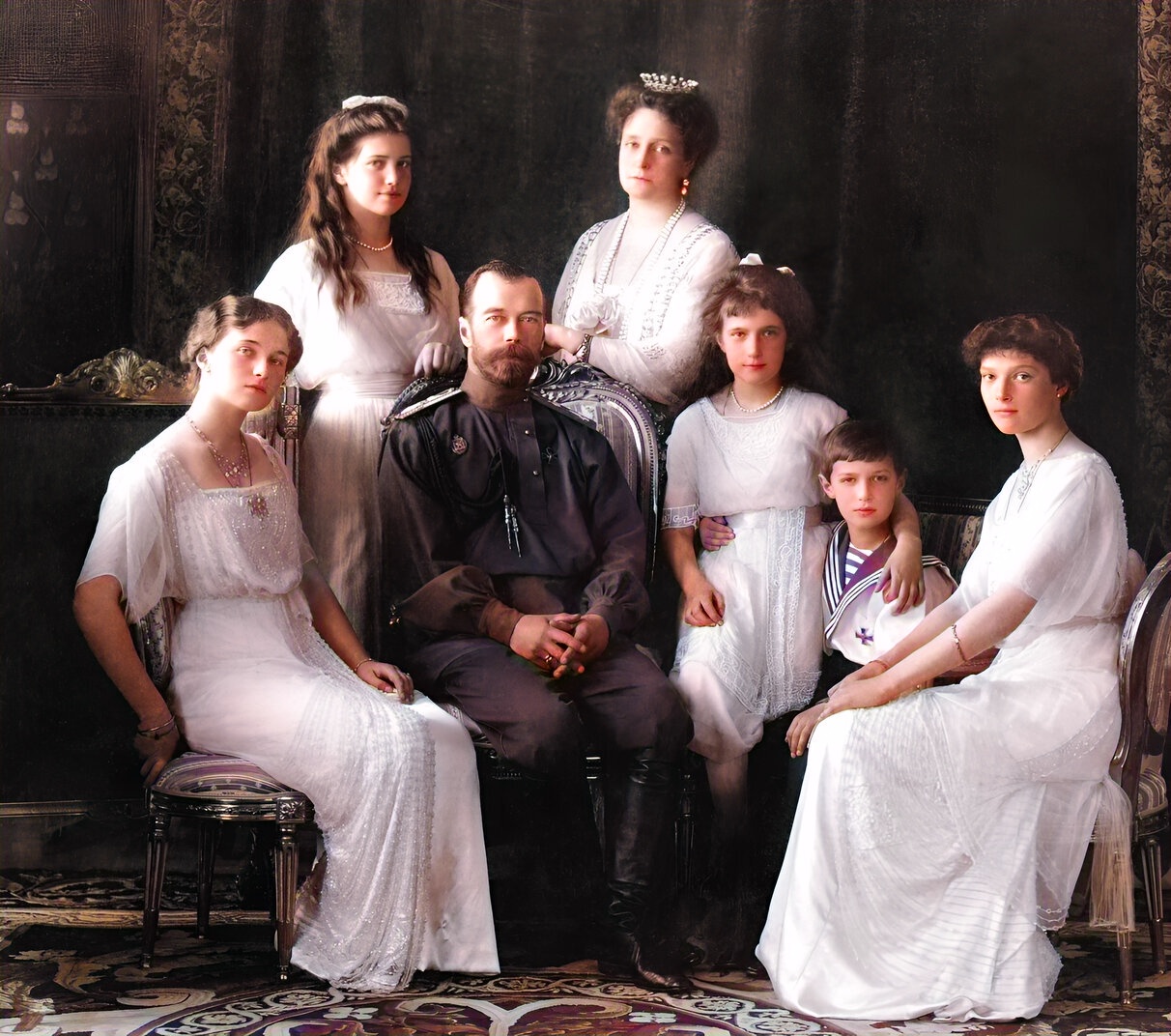
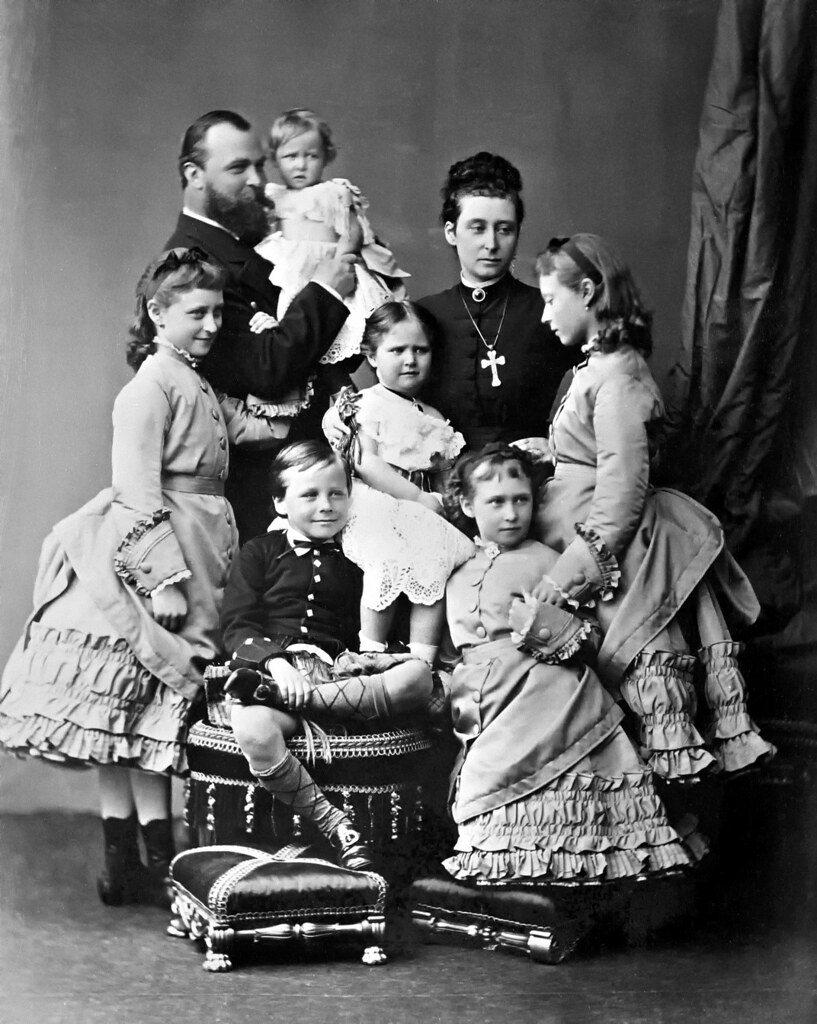
Against this backdrop were born two sisters—Princess Elisabeth, born 1864, and Princess Alix, born 1872.
They were part of a large noble German family of seven children.

But there was something connecting Elisabeth and Alix in particular.
It was as though they were marked by the hand of fate.
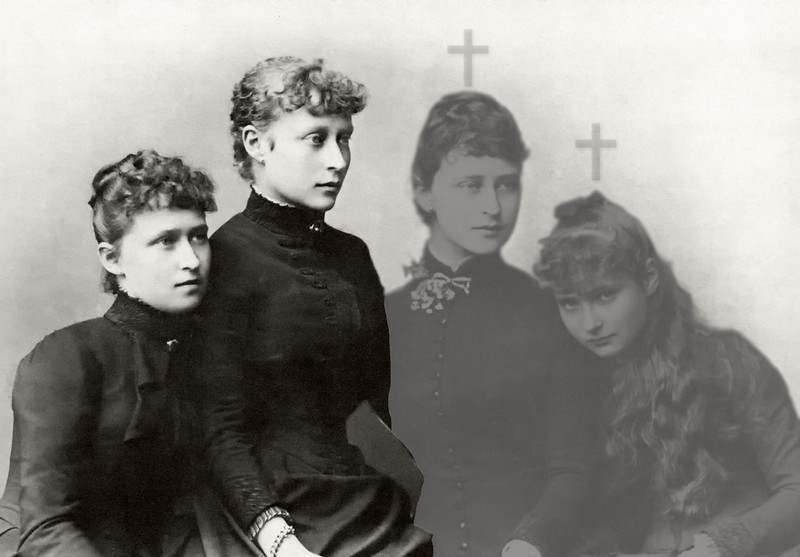
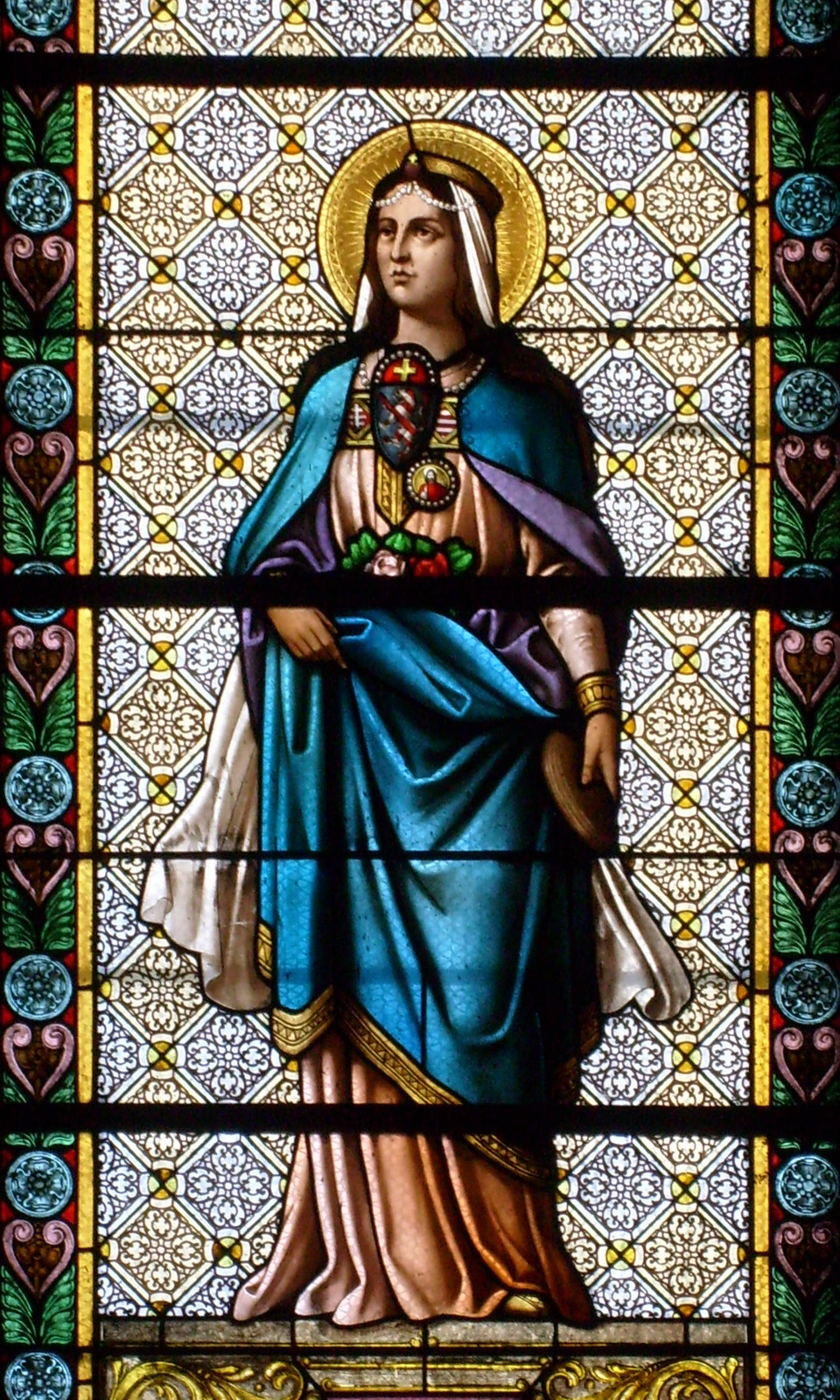
Princess Elisabeth of Hesse and by Rhine

Known as “Ella” within her family, Princess Elisabeth was named after St Elizabeth of Hungary, a princess herself and greatly venerated Catholic saint and patroness of the Third Order of St. Francis.
St Elizabeth, who was married at 14 and widowed at 20, built a hospital to serve the sick and became a symbol of Christian charity after her death just 4 years later.
The story of St Elizabeth would strangely touch the life of Princess Ella.

Growing up, she lived a modest life by royal standards, even though her father was from one of the oldest and noblest houses in Germany and her mother was Queen Victoria’s daughter.
She swept floors, cleaned her own room, and even accompanied her mother to care for soldiers at a nearby hospital when war broke out between Austria and Prussia.
Ella was charming and kind and considered to be one of the most beautiful of all the princesses in Europe.
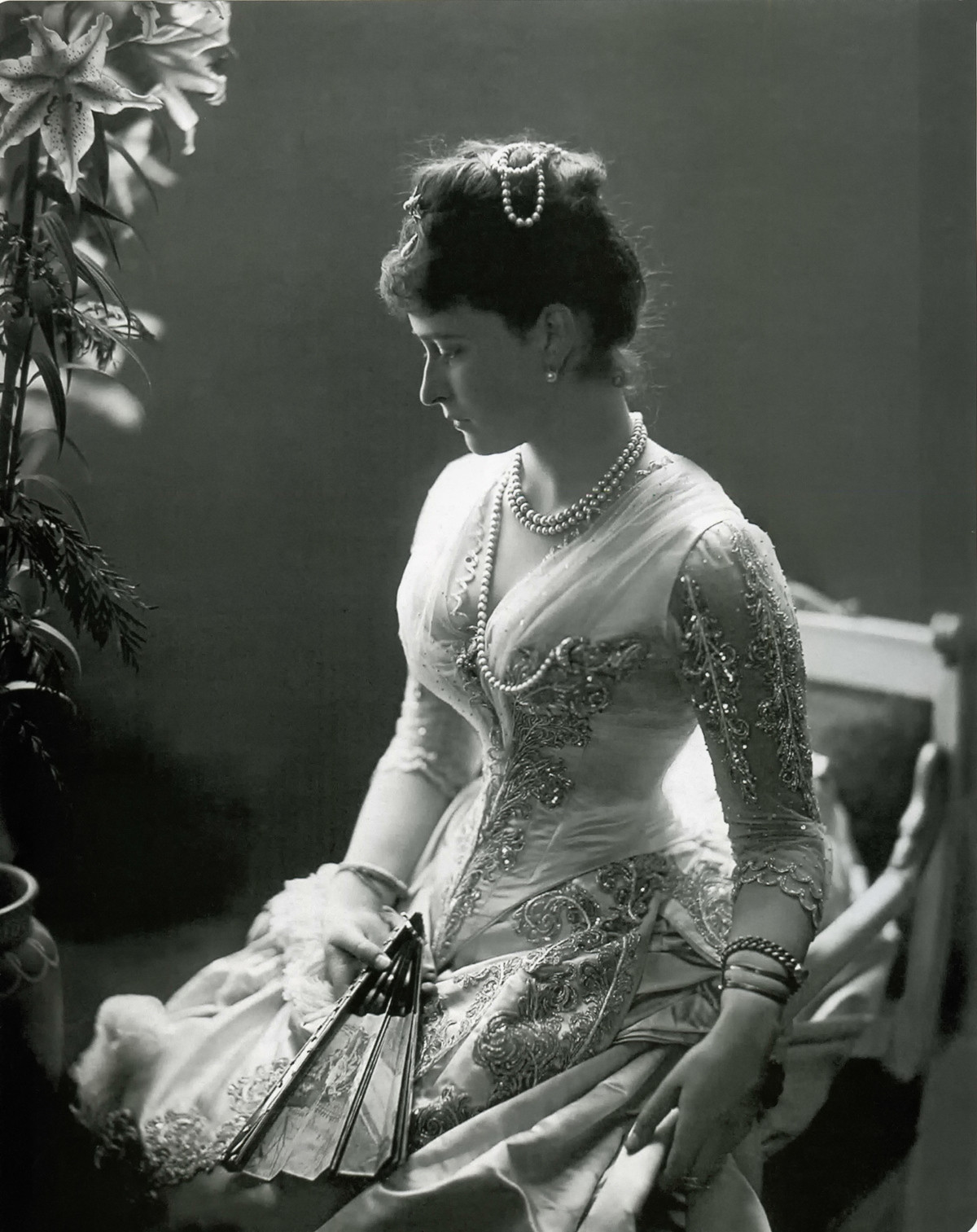

Frequently visiting his Hessian relatives and not failing to notice Ella’s beauty was her elder cousin, the young man who would later become the German Kaiser Willhelm II.
Writing and sending her numerous love poems, he fell in love with her and proposed in 1878.
One cannot help wondering how her life would have been different had she accepted.

Ella’s heart was eventually won by Grand Duke Sergei Alexandrovich of Russia—a choice her grandmother Queen Victoria did not approve of.
We must always listen to our grandmothers because they know things that we do not.
But such is young love.
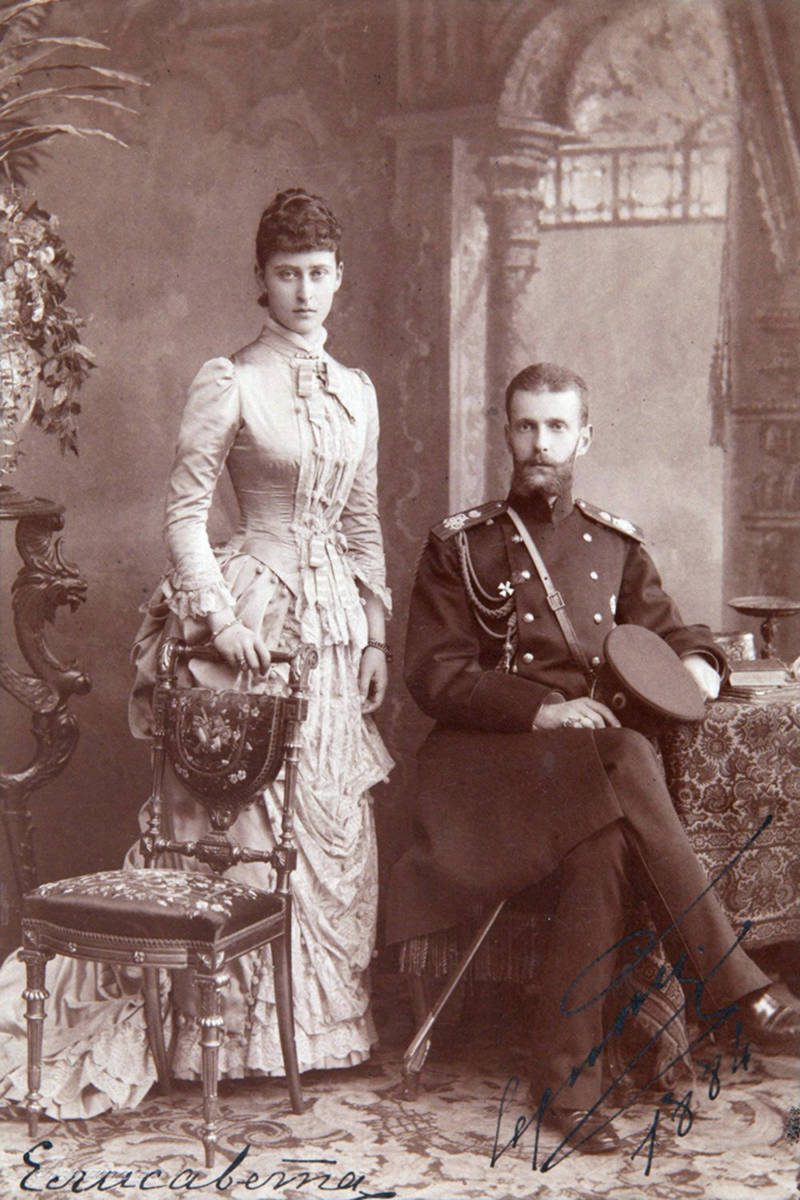

They were married in June 1884 and at the wedding, fate also struck her little sister when she met 16-year-old Nicholas, the future Tsar Nicholas II.
Residing in one of the Kremlin palaces and a summer home outside of Moscow, they lived happily, hosting frequent parties.
Ella encouraged the young Nicholas to pursue her sister Alix, again much to the dismay of Queen Victoria, who somehow had a sixth sense for what was coming.
Grandmothers know.
Then on a cold February morning of 1905, Ella’s husband Sergei was assassinated inside the Kremlin by a Socialist-Revolutionary.
Sergei had previously rounded up 20,000 Jews and evicted them from their homes for no reason and without warning.
Devoutly religious, Ella herself prophesized that “God will punish us severely”.
It was just the beginning.
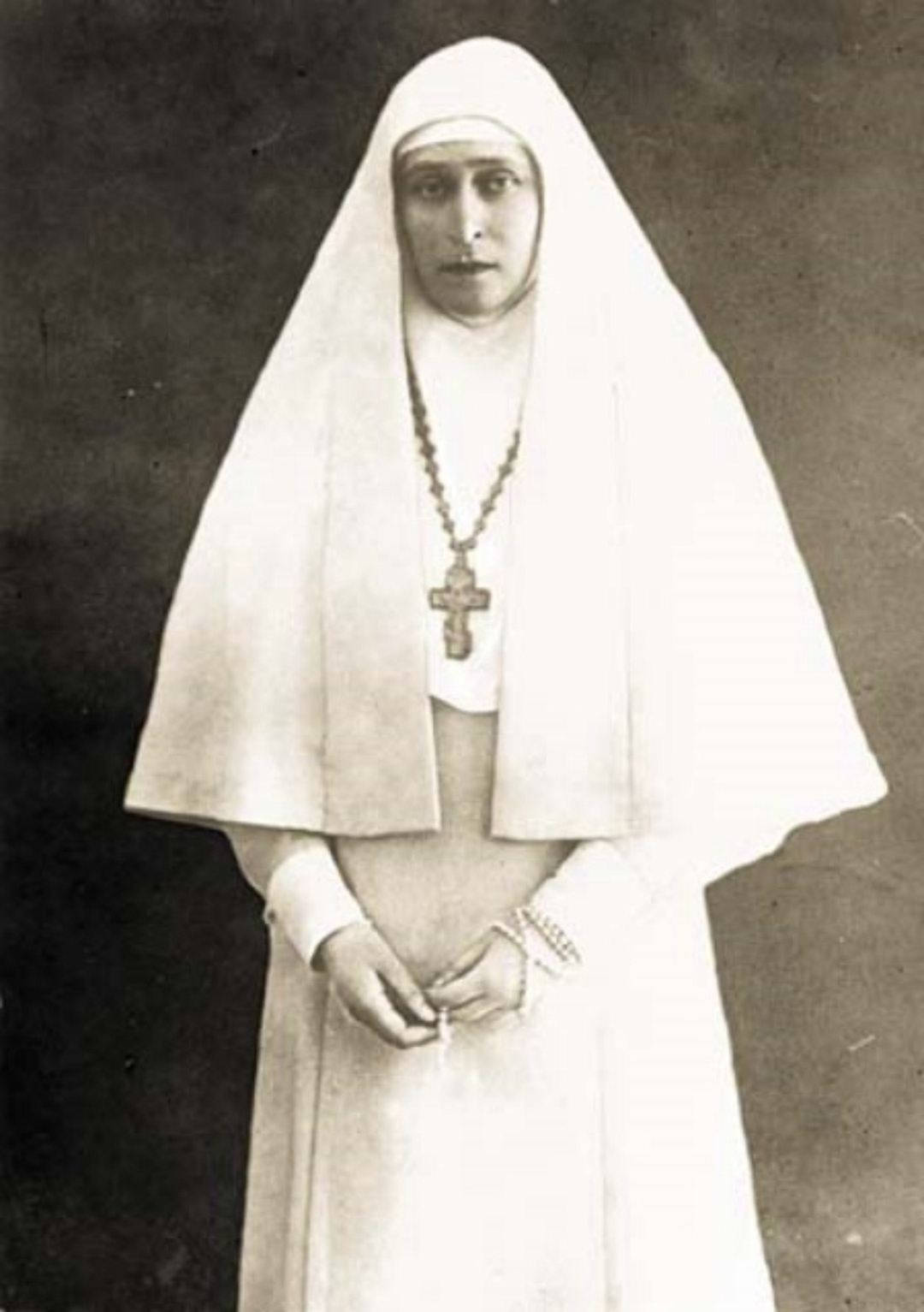

Consumed with sadness and guilt, Elisabeth became a devout nun.
Selling her possessions in 1909, she worked tirelessly for several years, helping the poor and sick in Moscow, often in the worst slums.
In 1916, Ella saw her sister for the last time.
The Murder of Elisabeth
It was July, 1918 when Lenin ordered the arrest of Elisabeth.
She spent a few days with other prisoners from Russian noble families before they were all carted to a small village with an abandoned mineshaft 66 ft deep.
Elisabeth was first.
She was beaten and hurled down the shaft.
Then the others followed and a hand grenade was thrown down to kill them, but only one man died.
According to one of the murderers, Elisabeth and the others survived the fall and after the grenade was tossed down, he heard Elisabeth and others singing a hymn.
Down went a second grenade and finally, brushwood shoved into the entrance and set alight.
After the revolution, her convent erected a statue of Elisabeth in the garden. It read simply:
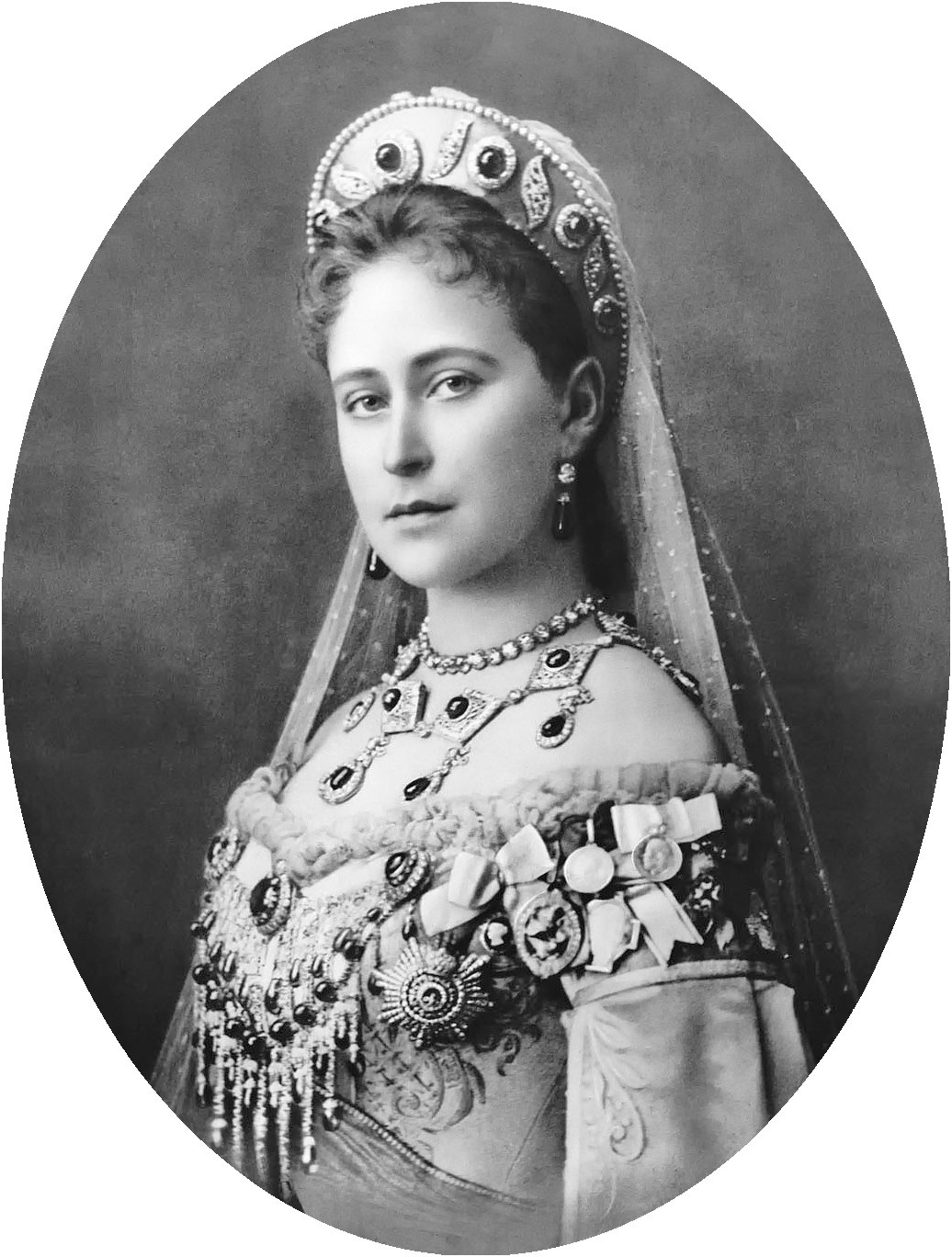
Princess Alix of Hesse and by Rhine
Sixth child among seven and the fourth daughter, Alix was nicknamed “Sunny” by her mother and “Alicky” by her British relatives so as to distinguish her from her aunt, Princess Alexandra of Denmark who would become Queen of England as the wife of Edward VII.
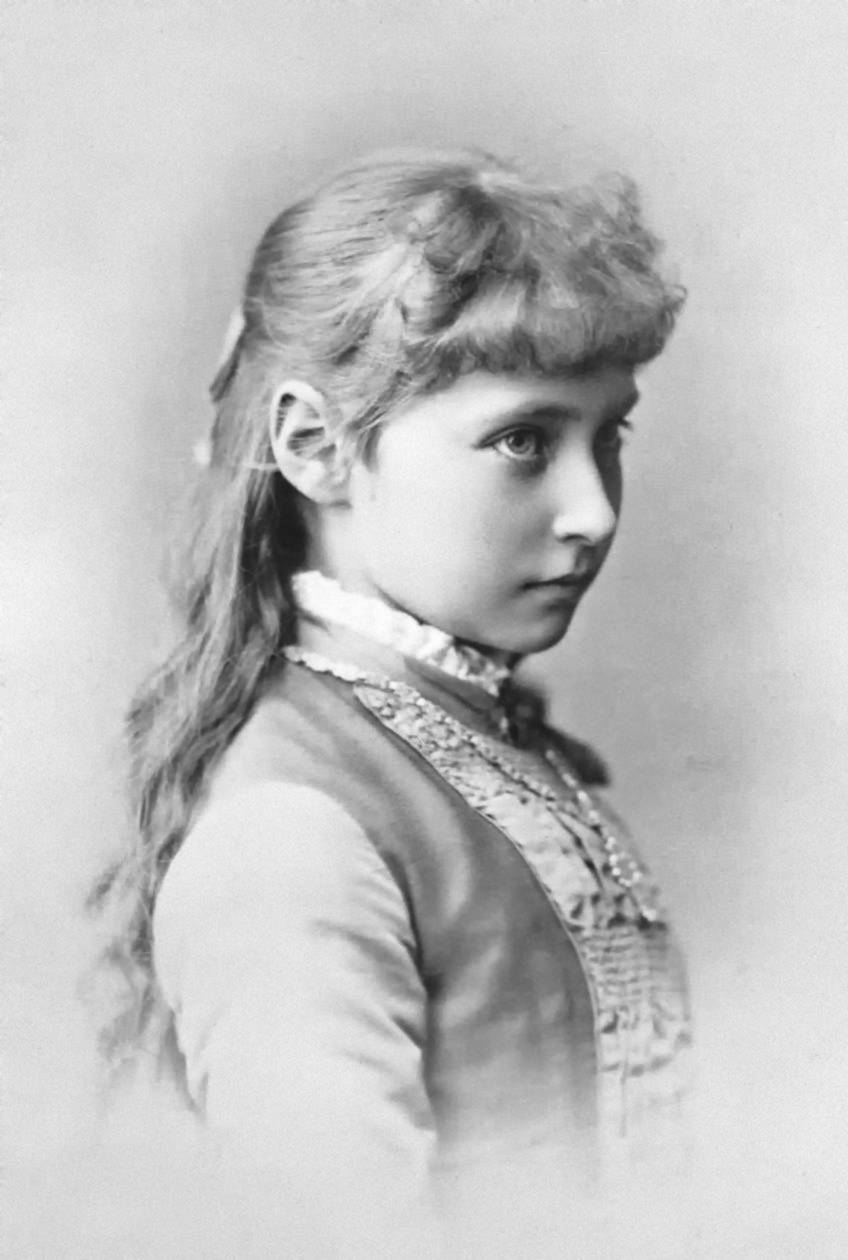

Blossoming into a beautiful young woman with sparkling blue eyes and red gold hair, she was Queen Victoria’s favorite granddaughter.
The Queen had her in mind to marry Edward Prince of Wales’s eldest son, Prince Albert Victor, Duke of Clarence and Avondale, thus securing her a future position as Queen of England.
What is it about grandmothers just knowing what is best for us?
A very different course of events awaited Alix as she was destined to marry Nicholas, the last Tsar of Russia.

Alix fell in love with Nicholas in 1889 and Nicholas wrote in his diary:
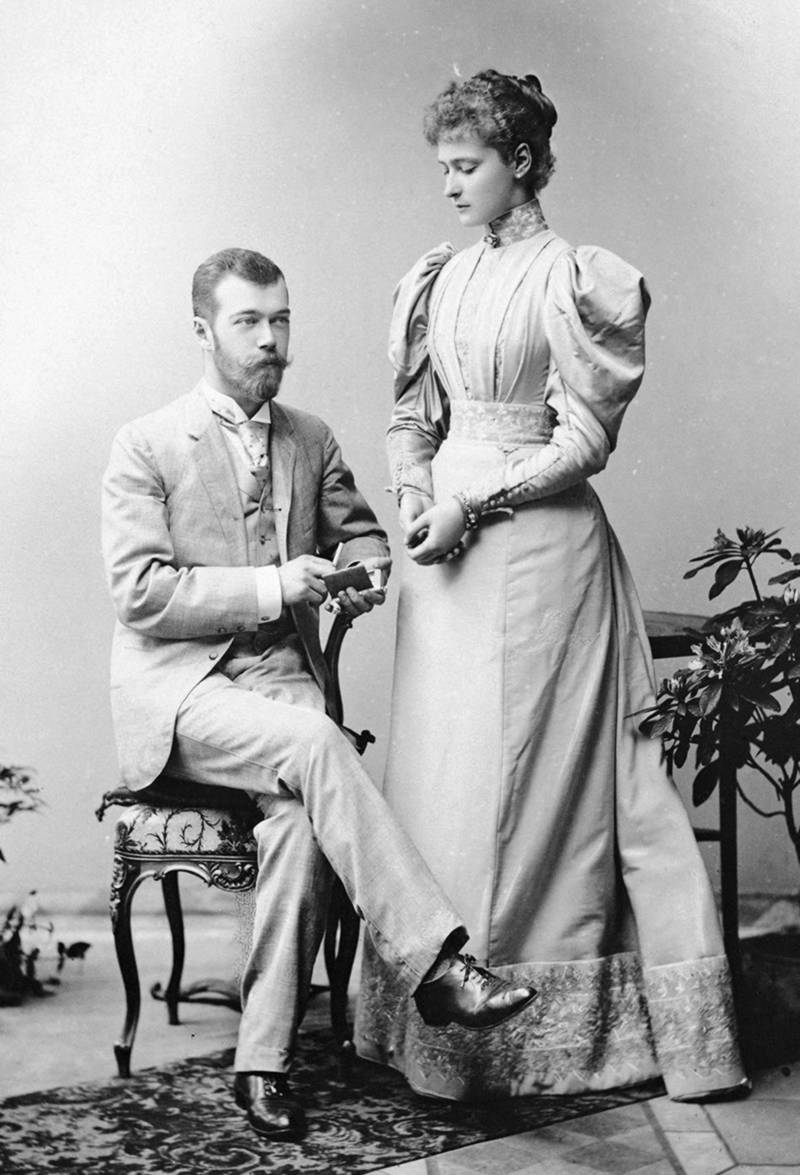

Nicholas had to propose twice because at first Alix did not want to convert to Russian Orthodoxy but was assured by her sister Elisabeth that it was very similar to her German Lutheranism.
After their engagement, Alix returned to England and was joined by Nicholas where they became godparents of the boy who would become the first British monarch to voluntarily abdicate the throne—King Edward VIII.
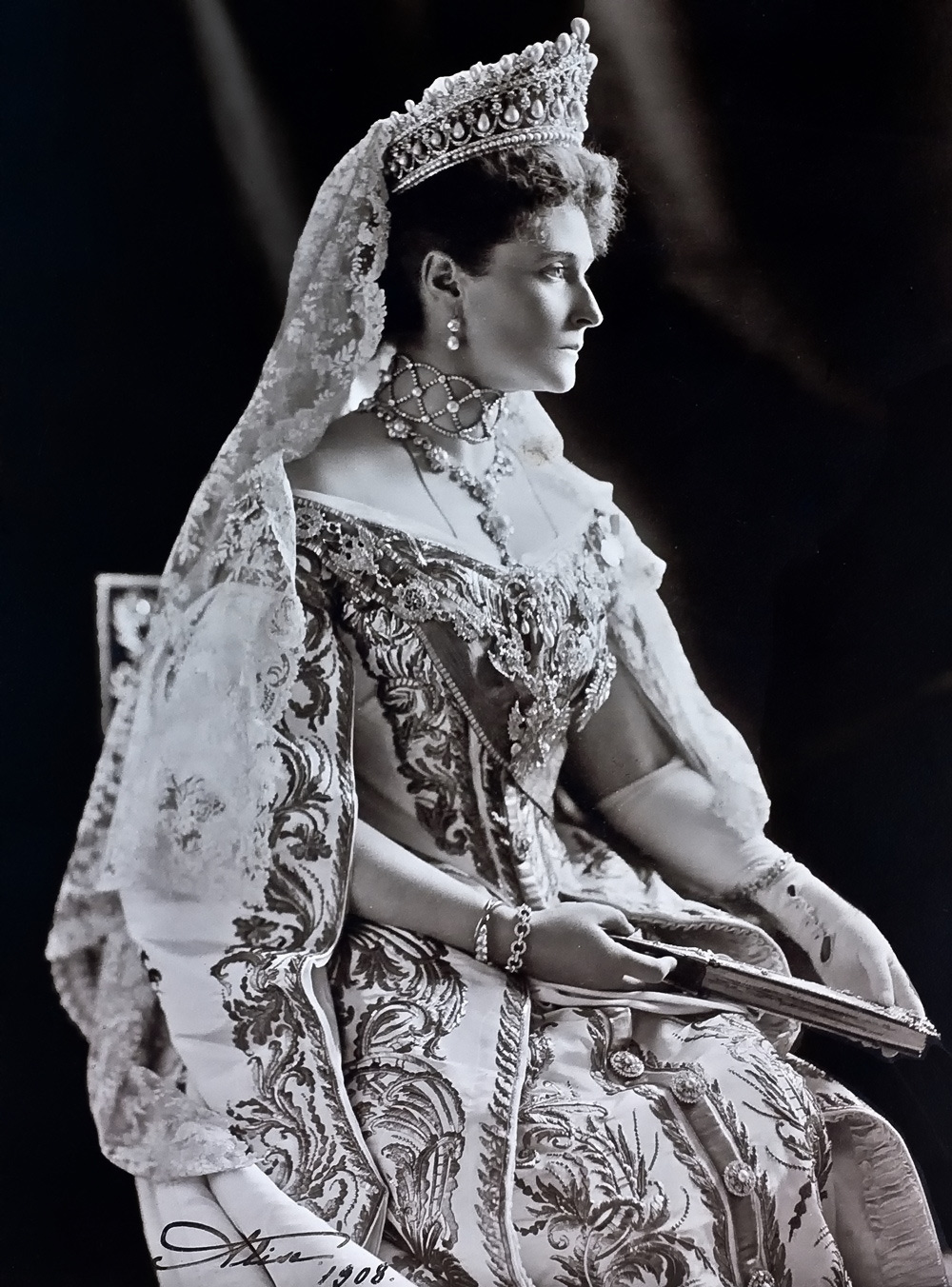

When Tsar Alexander III died in 1894, he left Nicholas as the new Emperor of Russia.
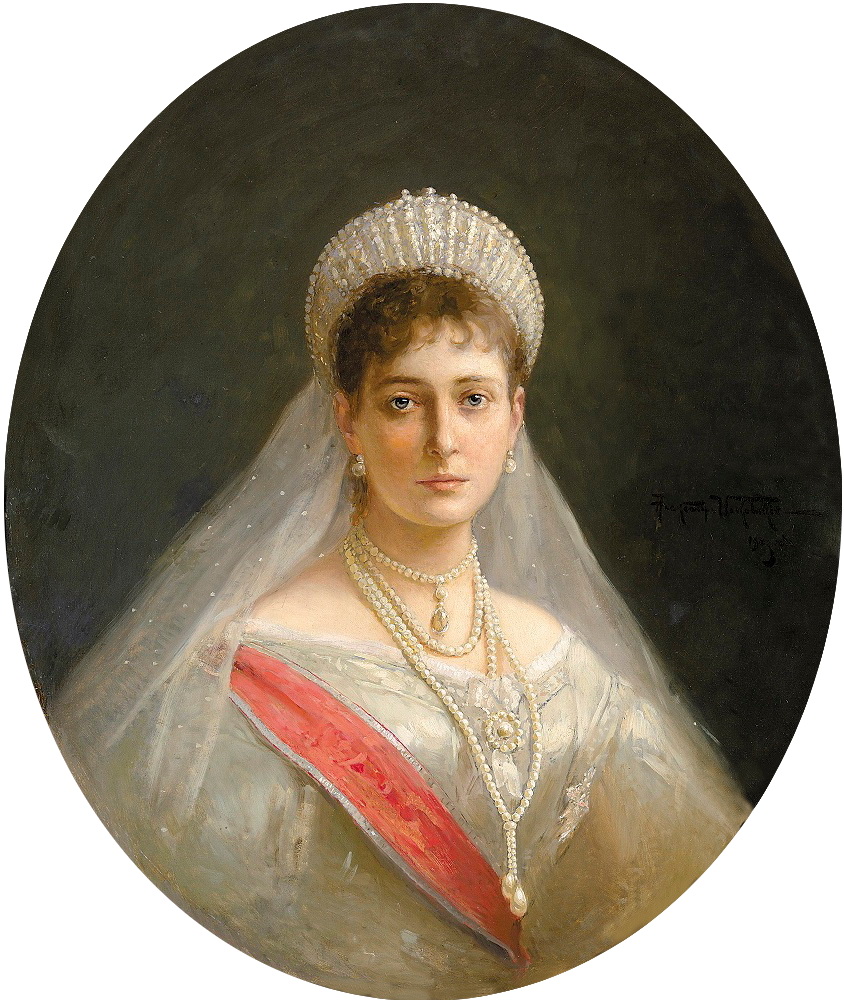
It was a whirlwind for Alix—she became Empress on her wedding day.
Shy and nervous, she was disliked from the beginning by the Russian people who saw her as cold and curt.
It set in motion a serious of events that would profoundly change the course of history.

Despite producing five beautiful daughters, the Russian people frowned upon her distaste for Russian culture and her inability to produce a male heir to the throne until Alexei, her little ‘sunbeam” arrived in 1904.
By this time, she had isolated herself from the Russian court, doting on her son and becoming a recluse.
She believed in the divine right of kings that it was not necessary to seek the approval of the people.
In a letter to her grandmother, Queen Victoria, her aunt wrote of her:
It was this thinking and her unwillingness to embrace her people that sealed her fate and that of her entire family.
The Murder of Alix
Dangerously weakened by World War I, Imperial Russia’s government could not bear the financial burden.
Mass hunger became the norm for millions of Russians who refused to accept it any longer and turned on their monarchy.
The entire family became prisoners in their own palace.
The provisional government hoped their foreign relatives might take them in.
Nicholas’s first cousin, George V of Great Britain, refused to offer the family asylum because the public sentiment was turning against royalty.
France was reluctant to accept them because the war with Germany was still raging and Alix was seen as a German sympathizer.
Hope abandoned the Romanovs.
The Bolsheviks seized power and moved the family to a more remote location.
It was Tuesday, 16 July 1918, a date that passed by peacefully without incident.
Nicholas walked with his daughters at 4 o’clock in the small garden.
Alix and Nicholas played cards until 10:30 and then retired to bed.
In the morning, everything changed.
Nicholas was shot in the chest several times and a bullet entered the left side of Alix’s skull just above her ear, exiting from the right side.
Their children were executed in a similar manner.
And that was the end of that.
Elisabeth and Alix were no more.
Two sisters caught up in the winds of change.
Two beautiful princesses whose lives were cut short because ideas changed.
And so it goes.
Why?
It is the oldest question known to mankind.
The mysteries of this world are often unfathomable.
But one thing is for certain.
The same question will continue to be asked until we find ways to live together in peace.